Chemical Profile of 2,6-Dimethoxyphenol: Structure, Properties, and Applications
2,6-Dimethoxyphenol (DMP) is a chemical compound commonly used in various industries. It plays an important role in pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and materials science. Understanding its chemical profile is essential for improving its applications. This compound has many uses due to its unique structure and properties. UniVOOK Chemical offers DMP as an organic intermediate in several grades and packaging options. We aim to meet the specific needs of our customers by providing the highest quality product. Additionally, we offer technical support to ensure the best performance of our product. UniVOOK Chemical’s Syringol is carefully batch-tested to guarantee consistent purity, particle size, and other important characteristics.
Chemical Structure and Characteristics
Molecular Formula: C8H10O3
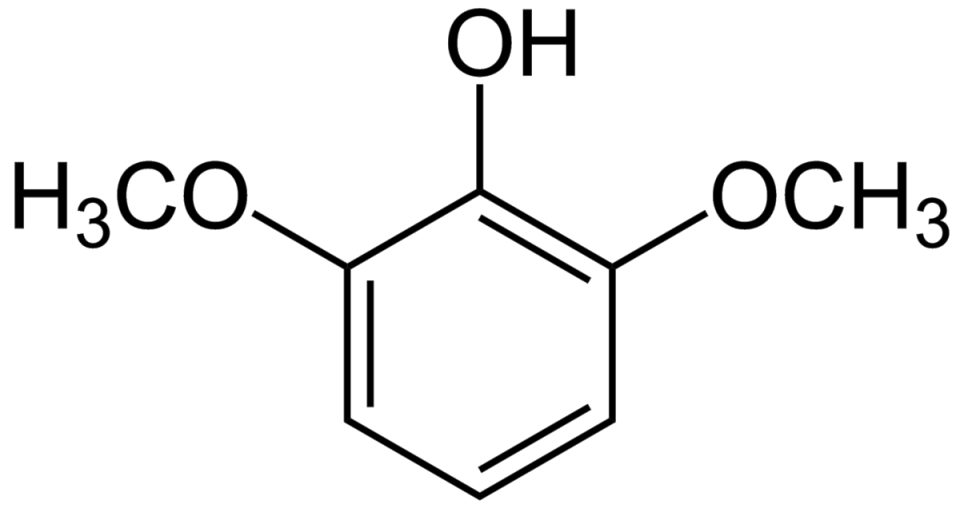
2,6-Dimethoxyphenol has the molecular formula C8H10O3, indicating it consists of eight carbon (C) atoms, ten hydrogen (H) atoms, and three oxygen (O) atoms.
Structural Overview
The structure of 2,6-Dimethoxyphenol features a benzene ring (a six-membered carbon ring) with two methoxy groups (–OCH3) attached at positions 2 and 6. These methoxy groups-comprising a carbon bonded to oxygen, which in turn is bonded to a hydrogen-are crucial in shaping the compound’s chemical behavior.
Chemical Properties
The compound is reactive due to its hydroxyl (–OH) and methoxy groups. The hydroxyl group is involved in hydrogen bonding and can undergo reactions like oxidation and esterification. The methoxy groups, by altering the electron density of the benzene ring, influence both solubility and reactivity. While 2,6-Dimethoxyphenol is generally stable under normal conditions, it can degrade in strongly acidic or basic environments.
The compound is soluble in various solvents such as alcohols, ethers, and chloroform, but less soluble in water-common for many phenolic compounds. Solubility is influenced by temperature and the polarity of the solvent.
Comparison with Other Phenolic Compounds
Compared to simpler phenolic compounds like phenol (C6H5OH), 2,6-Dimethoxyphenol contains two methoxy groups. These additional groups enhance the electron density on the benzene ring, influencing reactivity, especially in reactions like electrophilic aromatic substitution. The methoxy groups also affect its utility in industrial applications, making it more reactive than simpler phenols.
Physical Properties
Melting/Boiling Points
2,6-Dimethoxyphenol has a melting point between 56 – 58°C and a boiling point around 244°C. These values offer insights into the compound’s behavior under different conditions: its relatively low melting point allows easy handling at room temperature, while its high boiling point means it remains stable during processes involving higher temperatures.
Color, Odor, and Other Sensory Characteristics
In its pure form, 2,6-Dimethoxyphenol is a white to light brown powder. It has a mild odor, not overly strong or pungent, making it less likely to cause irritation compared to some other chemicals. Its appearance and scent may shift with storage conditions or impurities.
Solubility and Volatility
The compound is more soluble in organic solvents (alcohols, ethers) than in water. This makes it practical for use in industrial applications, where it can easily blend into different formulations. While it is not highly volatile, its volatility can increase at high temperatures or in low-pressure environments.
Synthesis of 2,6-Dimethoxyphenol
Overview of Common Synthetic Routes
2,6-Dimethoxyphenol can be synthesized using multiple methods. A common route involves the methylation of phenol with methanol and a catalyst. Another approach uses halogenated precursors that are reacted with methoxide to position the methoxy groups at the desired locations on the phenol ring. Each method has its own advantages depending on factors like purity, scale, and efficiency.
Key Reagents and Catalysts
Key reagents in the synthesis include phenol, methanol, and methoxide ions. Catalysts such as methylating agents or bases like sodium hydroxide are typically used to drive the reaction. The specific choice of reagents and catalysts depends on factors like reaction speed, yield, and environmental impact.
Potential Environmental or Economic Advantages
Different synthesis techniques offer varying environmental and economic benefits. For instance, some methods employ less toxic solvents or operate under milder conditions, making them more environmentally sustainable. On the economic side, more efficient processes can lower production costs by reducing energy consumption or simplifying purification steps.

Applications in Industry
Pharmaceutical Industry
2,6-Dimethoxyphenol serves as a valuable intermediate in drug synthesis, particularly for bioactive compounds. Its structural properties, including the methoxy groups, can enhance drug bioavailability and stability, making it essential for designing pharmaceuticals that target specific biochemical pathways.
Agricultural Industry
In agriculture, this compound is utilized in pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides due to its ability to interfere with the growth of pests, fungi, and weeds. Its effectiveness in controlling a wide range of agricultural threats makes it an essential ingredient in crop protection products.
Cosmetics and Personal Care
The antioxidant properties of 2,6-Dimethoxyphenol make it beneficial in cosmetics and personal care items. It is often incorporated into skincare products to protect against oxidative stress, a major contributor to aging and skin damage. The compound’s mild sensory characteristics also make it well-suited for use in products where fragrance and texture are important.
Material Science
In material science, 2,6-Dimethoxyphenol is being explored for its potential in polymer chemistry. It can be used as a precursor for specialized chemicals and is involved in creating materials with tailored properties. Its unique structure allows for modifications that could lead to higher-performance polymers or coatings.
Other Niche Applications
Beyond the major industries mentioned, 2,6-Dimethoxyphenol has niche applications in dyes, fragrances, and other specialized sectors. Its ability to interact with various chemicals makes it useful for producing specific dyes and fragrances with desirable properties.
Final Thoughts
2,6-Dimethoxyphenol is a powerful compound with many uses in industries like pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and materials science. It is a key ingredient for drug synthesis, crop protection, and skincare formulations. At UniVOOK Chemical, we provide high-quality 2,6-Dimethoxyphenol in different grades to meet your needs. Our product is tested for purity and performance. Whether you’re in research, production, or development, we can support your goals. Get in touch with us today to learn more and place your order!
Access Our Product Catalog and More to Discover High-Performance Chemicals Tailored to Your Business Needs