Ethylenebisstearamide (EBS) in Focus: Properties, Applications, and Market Insights
Ethylenebisstearamide (EBS)(CAS No. 10-30-5) is an extensively utilized amide wax renowned for its exceptional lubricating properties. It functions as both an internal and external lubricant, mold release agent, dispersant, and slip- and anti-blocking agent. Its primary application lies in enhancing materials like ABS, PS, PP, and others within the plastics industry. Moreover, EBS plays a crucial role in industries such as coatings, inks, rubber, and textiles, where its distinct characteristics significantly enhance processing efficiency and product performance.
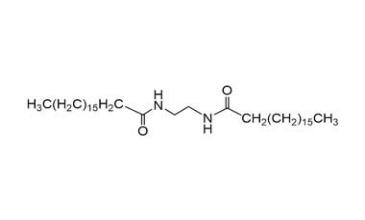
Chemical Properties of EBS
Molecular Structure and Formula
Ethylenebisstearamide (EBS) is a synthetic wax formed from the reaction of ethylenediamine with stearic acid, resulting in a molecular formula of C38H76N2O2. This structure consists of two lengthy hydrocarbon chains linked by an ethylene diamide group, imparting distinctive properties essential for its varied applications.
Physical Properties
EBS exhibits a melting point range of approximately 140-145°C, rendering it suitable for high-temperature applications. It demonstrates insolubility in water while displaying solubility in organic solvents like toluene and xylene. With its waxy texture and white to slightly yellowish appearance, EBS integrates seamlessly into diverse formulations across industries.
Chemical Stability and Reactivity
Known for its exceptional chemical stability, EBS maintains robust performance under various environmental conditions, resisting oxidation effectively. It exhibits non-reactivity with most chemicals, ensuring reliability as both a processing aid and additive in numerous industrial applications.
Features and Advantages of Ethylenebisstearamide (EBS)
- Lubricant in Polymer Processing:
EBS serves as a highly effective lubricant for polymers such as ABS, AS, hard PVC, polyformaldehyde, polycarbonate, polyurethane, and phenol-formaldehyde resins. Its dual role as an internal and external lubricant enhances processing efficiency, particularly in demoulding applications where concentrations of 0.5-1.5% are recommended.
- Anti-Adhesive Agent for Polymer Films:
In polymer films and sheets, EBS functions as an anti-adhesive agent, preventing air bubble formation and imparting slipperiness to plastic bags at concentrations of 0.5-1%, facilitating easier handling and opening.
- Enhancer of Heat-Resistant and Weather-Resistant Properties:
EBS significantly improves the heat and weather resistance of polymers, especially when combined with inorganic fillers in formulations for PVC and polyolefins. Its ability to enhance dispersion and coupling properties with pigments and fillers contributes to heightened product durability and performance.
- Nucleation Transparency Agent:
Used in polyolefins, polyformaldehyde, and polyamide, EBS acts as a nucleation transparency agent, reducing nucleation time, refining resin structure, and enhancing mechanical properties and transparency in final products.
- Enhancer in Synthetic Fiber Industry:
EBS plays a pivotal role in enhancing heat and weather resistance in polyester and polyamide fibers. It reduces yarn breakage during antistatic nylon fiber spinning, thereby enhancing overall production efficiency and product quality.
- Processing Auxiliary in Rubber Industry:
In rubber processing, EBS serves as a processing aid, improving demoulding properties and modifying filler performance. It also enhances surface smoothness in rubber products, serving as an effective polishing agent.
- Coating Additive for Improved Properties:
As an additive in coatings, EBS improves pigment and filler dispersion, enhances surface leveling properties, and increases resistance to water, acids, and alkalis. Its inclusion in nitrocellulose lacquers provides a flatting effect, enhancing the aesthetic and protective qualities of coated surfaces.
- Lubricant in Powder Metallurgy (PM):
EBS functions as a lubricant in powder metallurgy applications, reducing inter-particle and die-wall friction during compaction. This improves powder compressibility and facilitates easier component ejection from moulds, enhancing manufacturing efficiency.
- Paper-Making Industry:
In paper-making, EBS acts as a defoamer and anti-foaming agent, improving paper quality by reducing foam formation during production. It also serves as a coating component, enhancing surface characteristics and printability.
- Dope and Oil Paint Additive:
EBS enhances the salt mist and damp-proof effects in dope and oil paints, improves paint removal performance, and acts as a dulling agent for furniture polishing and printing ink applications. Its wear-resistant and smoothing properties contribute to enhanced surface finishing and air release in porous materials.

Applications of EBS
Additive in Polymers
Ethylenebisstearamide (EBS) can be seamlessly integrated into polymers to prevent undesired adhesion, particularly under high temperatures and pressures. It inhibits the sticking of adhesive granules during storage and prevents the attraction of dirt or cohesion of adhesive film layers before application. Additionally, EBS enhances the dispersion of fillers in polymer matrices, improving overall material performance.
Binder and Dispersant
Beyond plastics, EBS serves as a binder in precision engineering for metal parts. Its excellent dispersing ability and surface migration make it valuable in the formulation of printing inks, contributing to improved ink properties. This enhances the quality and durability of printed materials, making EBS a crucial component in the printing industry.
Asphalt Modifier
In the bitumen industry, EBS acts as an asphalt modifier. When incorporated into asphalt binders for road construction, it elevates the softening point and enhances visco-elasticity. This results in increased durability and performance of asphalt mixtures, ensuring longer-lasting and more resilient road surfaces.
Market Insights
Global Market Dynamics
The global Ethylenebisstearamide (EBS) market is experiencing robust growth, driven by its versatile applications across industries such as plastics, rubber, and coatings. The increasing demand for high-performance lubricants and processing aids underscores its pivotal role in enhancing manufacturing efficiency. With advancements in technology and a growing focus on sustainability, the EBS market is poised for sustained expansion in the foreseeable future.
Drivers and Challenges
Key drivers of the EBS market include the escalating need for superior polymer quality and efficient manufacturing processes. However, challenges like volatile raw material costs and stringent environmental regulations pose significant hurdles. Manufacturers are actively developing eco-friendly EBS variants to navigate these challenges while complying with regulatory standards.
Regional Market Analysis
North America and Europe lead the EBS market, driven by robust demand in automotive, construction, and packaging sectors that favor advanced materials. In contrast, rapid industrialization and urbanization in Asia-Pacific, particularly in China and India, present burgeoning opportunities. Local manufacturers are scaling up production capacities to meet escalating regional demand, highlighting dynamic growth prospects in these emerging markets.
Environmental and Regulatory Considerations
Environmental Impact
EBS production and utilization exhibit a relatively low environmental footprint compared to alternative chemical additives. Nonetheless, it is crucial to assess and mitigate potential environmental risks associated with its lifecycle, from manufacturing to disposal. Industry players are increasingly adopting sustainable practices to minimize ecological impacts and enhance environmental stewardship.
Regulatory Landscape
Stringent regulatory frameworks govern the EBS industry to ensure environmental safety and regulatory compliance. Adherence to international standards such as REACH and stringent local regulations is imperative for market participants. Continuous monitoring and compliance initiatives are vital to uphold market integrity and consumer confidence.
Future Outlook
Emerging Trends and Innovations
The future of EBS is shaped by its expanding applications in bioplastics, sustainable coatings, and advanced composites. Ongoing research and development focus on enhancing EBS’s functional properties to align with evolving industry requirements. Innovations are driving new growth avenues, positioning EBS as a pivotal component in next-generation materials.
Market Forecast and Growth Opportunities
The EBS market is poised for sustained growth, supported by technological advancements and increased investment in R&D. Emerging economies present significant growth opportunities, coupled with expanding applications across diverse industrial sectors. Market forecasts indicate a positive trajectory, with adaptable companies poised to capitalize on evolving market dynamics and drive substantial growth.
Closing Thoughts
Ethylenebisstearamide (EBS) stands out as a versatile amide wax celebrated for its exceptional lubricating properties and broad industrial applications. Its efficacy as a lubricant, mold release agent, dispersant, and anti-blocking agent is invaluable in enhancing plastics such as ABS, PS, and PP. Moreover, EBS plays a crucial role in coatings, inks, rubber, and textiles, significantly boosting processing efficiency and product performance across these sectors. The global demand for EBS is on a robust growth trajectory, fueled by increasing applications across diverse industries and a growing emphasis on sustainability. Despite challenges like fluctuating raw material costs and stringent regulations, the market shows promise with expanding opportunities in bioplastics and advanced composites, driven by ongoing innovation and substantial investments in research and development.
Access Our Product Catalog and More to Discover High-Performance Chemicals Tailored to Your Business Needs