Thymol: Nature’s Antioxidants and Preservative for Food
Thymol, recognized chemically as 5-methyl-2-isopropylphenol, is predominantly sourced from the herb Thymus vulgaris, commonly known as common thyme. As a monoterpene phenol, it exhibits remarkable antiseptic, antifungal, and antioxidant attributes, rendering it highly sought-after in medicinal and industrial sectors. Given the pivotal roles antioxidants and preservatives play in food preservation, thymol emerges as a versatile agent capable of not only extending shelf life and preserving quality but also potentially conferring health benefits upon consumers.
What is Thymol?
Definition and Natural Sources
Thymol, a monoterpene phenol, is a naturally occurring compound primarily sourced from the herb Thymus vulgaris, commonly referred to as common thyme. This aromatic herb is native to regions around the Mediterranean and is widely cultivated for its culinary and medicinal properties.
Chemical Structure and Properties
Thymol, chemically known as 5-methyl-2-isopropylphenol, boasts a unique molecular structure characterized by its phenolic ring and methyl and isopropyl groups. This structure contributes to its distinctive properties, including its potent antiseptic, antifungal, and antioxidant capabilities.
UniVOOK Chemical: Your Trusted Source
UniVOOK Chemical is dedicated to providing top-quality chemicals for various industrial applications, adhering to strict quality standards to ensure purity and efficacy in every batch. Trust UniVOOK Chemical for a reliable source of food and feed-grade synthesized Thymol tailored to meet your specific requirements.
Antioxidant Properties of Thymol
Explanation of Antioxidants and Their Role in Health
Antioxidants are compounds that help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, thereby protecting cells from oxidative damage. By combating oxidative stress, antioxidants play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions.
Mechanisms of Thymol as an Antioxidant
Thymol exerts its antioxidant effects through various mechanisms, including scavenging free radicals, enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidants like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, and chelating transition metal ions involved in oxidative reactions. Additionally, thymol may modulate signaling pathways associated with inflammation and oxidative stress, further contributing to its antioxidant properties.
Research Findings on Thymol’s Antioxidant Effects
Numerous studies have investigated the antioxidant potential of thymol and its implications for health. Research suggests that thymol exhibits significant free radical scavenging activity, effectively protecting against oxidative damage to lipids, proteins, and DNA. Moreover, thymol has been shown to mitigate inflammation and oxidative stress in various experimental models, highlighting its therapeutic potential in combating oxidative-related diseases.
Thymol: Enhancing Food Preservation
Necessity of Food Preservation
Preserving food is vital for prolonging its shelf life, upholding quality, and averting spoilage and foodborne illnesses. In our interconnected global food supply chain, effective preservation methods are indispensable to ensure food safety and security.
Thymol’s Mechanism as a Preservative
Thymol functions as a potent antimicrobial agent, thwarting the proliferation of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms responsible for food spoilage and contamination. Its ability to disrupt microbial cell membranes and metabolic processes renders it efficacious in preserving the freshness and safety of diverse food items.
Practical Applications and Instances of Thymol in Food Preservation
Thymol finds widespread application in food preservation across various products such as meats, dairy items, baked goods, and beverages. Whether integrated into packaging materials, directly added to foods, or applied as a surface treatment, thymol effectively inhibits microbial growth. Examples include its utilization in meat curing, cheese production, and the preservation of fruits and vegetables.
Safety Precautions and Regulatory Compliance
While generally regarded as safe for food use, regulatory bodies like the FDA and EFSA have stipulated specific guidelines and maximum permissible limits to ensure thymol’s safe utilization. Adherence to these regulations and adherence to proper handling and storage practices are crucial to mitigating potential risks associated with thymol in food preservation.
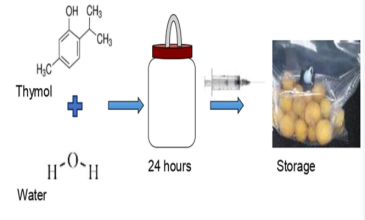
Harnessing the Health Benefits of Thymol in Food
Promoting Food Safety through Antimicrobial Action
Thymol’s robust antimicrobial properties bolster food safety by impeding the growth of pathogenic bacteria and fungi implicated in foodborne illnesses. By curtailing microbial contamination, thymol helps avert spoilage and extends the shelf life of perishable foods, thereby enhancing overall food quality and safety.
Potential Health Enhancements for Consumers
Beyond its preservative role, thymol may confer health benefits to consumers. Research indicates its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects, potentially supporting immune function, digestive health, and overall well-being when incorporated into a balanced diet.
Research Backing Thymol’s Utility in Food
Numerous studies have scrutinized thymol’s efficacy as a food preservative and its potential health impacts. Evidence suggests that thymol proficiently restrains the growth of foodborne pathogens like Salmonella, Escherichia coli, and Listeria monocytogenes, while simultaneously augmenting the sensory attributes and nutritional value of preserved foods.
Exploring Thymol’s Culinary Versatility
Flavor Profile and Culinary Heritage
Thymol infuses dishes with a distinctive flavor profile characterized by its aromatic, herbaceous, and subtly peppery notes. Integral to Mediterranean cuisine, it embellishes meats, stews, soups, and sauces, underscoring its versatility and widespread culinary appeal.
Creative Methods for Incorporating Thymol in Cooking
Fresh or dried, thymol enriches a plethora of dishes, complementing meats, poultry, fish, vegetables, and legumes with its aromatic essence. Thyme-infused oils, vinegars, and marinades also feature prominently in culinary creations, adding depth and complexity to various recipes.
Inspiration for Culinary Innovation with Thymol
From timeless classics like garlic and thyme roast chicken to inventive concoctions such as thyme-infused cocktails and desserts, the culinary possibilities with thymol are boundless. Embrace experimentation with diverse flavor combinations and cooking techniques to unlock thymol’s unique culinary potential.
Future Directions and Conclusion
Thymol emerges as a remarkable compound, offering a dual role as both a natural antioxidant and an effective food preservative. With its potent antimicrobial properties and potential health benefits, thymol not only enhances food safety and shelf life but also contributes to overall well-being. As a versatile ingredient in culinary traditions worldwide, thymol enriches dishes with its distinct flavor profile, inspiring culinary creativity. With ongoing research uncovering its diverse applications and benefits, thymol stands as a testament to nature’s capacity to provide solutions for food preservation and health promotion. Embracing thymol as nature’s antioxidants and preservative for food underscores the importance of harnessing natural compounds for sustainable and wholesome food practices.
Access Our Product Catalog and More to Discover High-Performance Chemicals Tailored to Your Business Needs